Content
About the application
GreenBro is a personal assistant that allows you to learn more about your device, as well as about existing system and installed applications.
Application functions:
- view the number of installed and system applications on the device;
- display of the level of charge and temperature of the battery of the device;
- View information about the device (model, manufacturer, version android).
For the application is available:
- Share the Apk file;
- launching the application;
- View the application manifest;
- Exporting the Apk-file to external storage;
- View the report on the permissions of the application;
- uninstall the application;
- Check for availability on Google Play and F-Droid;
- View the date of installation and update of the application;
- View service information about the application;
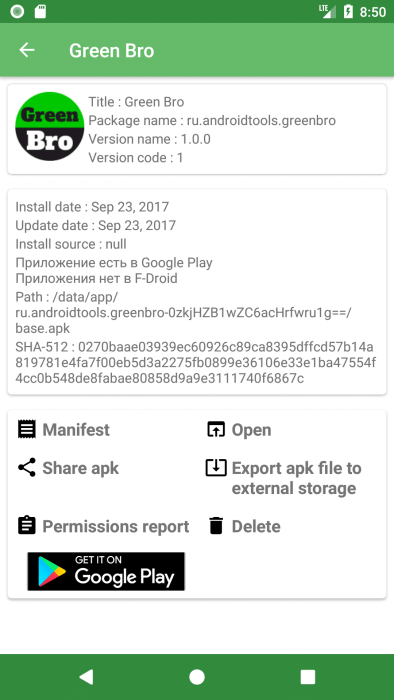
- Calculation of SHA-512 for Apk-file.
The application is at the stage of active development. Your comments and suggestions can be sent to rusdelphi@gmail.com
Getting information about the right application
If you want to know how safe the application you are using, then you can select it in the list of installed applications by opening GreenBro. The resulting screen will display all the collected information about the application and APK , such as: the date the application was installed and its update, its version and package name.
The presence of the application in the market is checked because if the application was removed from the market for any reason, it could violate the rules of this market and be potentially dangerous for users.
In addition to the usual functions of opening / removing the application, using GreenBro you can:
- View application manifest
The application manifest is an XML file containing important information about the application, such as:- Requested permissions
- Requested features
- Application settings: icons, themes;
- List of activity of the application;
- List of broadcast receivers.
Knowing the requested permissions is extremely important: if a simple application requests permissions that seem to be completely unnecessary, then perhaps this application can be dangerous.

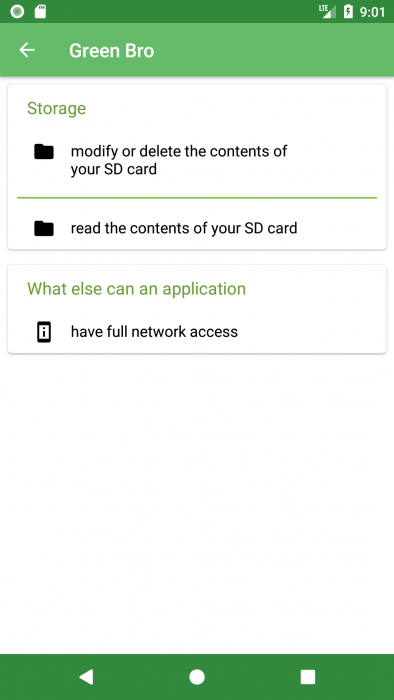
- See which permissions the application requests from Android
A separate point is the application permissions, which are presented in a form that is convenient for viewing. The permissions themselves are divided into categories.
- Share or export an APK application file
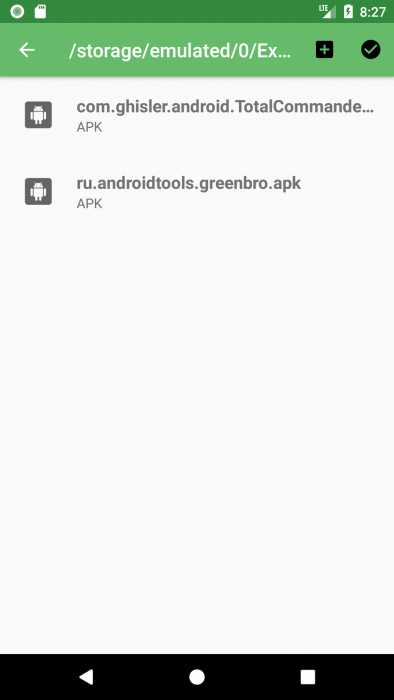
If you want to send someone to APK you can share it with friends or acquaintances via messengers \ mail \ other applications or you can save yourself an APK file on the SD card, which you can then copy. for example, a computer. To do this, you need to click on “Export APK to external storage“, after which you will receive a notification of successful or not successful completion of the operation. While using this function, the application can ask you for permission to read and modify data on external storage, this is necessary for that. so that the application can write the APK to the SD card.
By default, all APKs are copied to the <external storage>/ExtractedApks directory, however you can change the path if desired. To do this, enter the settings in the application menu, click on “Saved path”, and then a new activity will open, in which you can select the destination folder or create your own.
Android OS Versions
| Version | Name | API version | Release date |
| 1.6 | Donut | 4 | 2009 |
| 2.1 | Eclair | 5-7 | 2010 |
| 2.2 | Froyo | 8 | 2010 |
| 2.3 | Gingerbread | 9-10 | 2010 |
| 3.0 | Honeycomb | 11-13 | 2011 |
| 4.0 | Ice cream sandwich | 14-15 | 2011 |
| 4.1 | Jelly Bean | 16-18 | 2012 |
| 4.4 | KitKat | 19 | 2013 |
| 5.0 | Lolipop | 21-22 | 2014 |
| 6.0 | Marshmallow | 23 | 2015 |
| 7.0 | Nougat | 24-25 | 2016 |
| 8.0 | Oreo | 26 | 2017 |
Installed and system applications
In Android, in addition to the applications that you install yourself from the market, there are also applications that are initially installed in the firmware of the device.
Such applications are called system applications. They can be both vital to the system (for example, the application keyboard), and completely useless. Each manufacturer decides which applications to install in the firmware of the device.
System applications can be stopped by going into the device settings, but you need to do this carefully, as this can lead to a malfunction in the operation of Android.
To remove system applications simply does not work, you need to get root-rights on the device. To get them, you can either reflash the device manually, or install specialized programs. In some cases, this is necessary, since viruses can be registered in system applications and thereby gain full access to the device.
Internal and external device memory
The Android phone has various types of internal memory and external storage memory.
1. RAM (RAM)
RAM (RAM) is a “random access” memory, that is, a so-called RAM where the software writes and reads information quickly (and without emulation). The contents of the main memory will be cleared if the power fails, for example, if the phone is turned off. The amount of RAM decides how many applications can be run simultaneously, or how a large file can be loaded into memory for work (viewing, editing, etc.). An “Insufficient memory” error may occur if the memory is exhausted and the program can not be started.
2. ROM (ROM)
ROM (ROM) is a read-only memory. What is stored in it can never be changed (it is recorded once when the phone is made). ROM stores data even without power.
In the Android-phone ROM is divided into several sections. One part for OS (operating system). The OS partition is protected, and you can not write to it without root authority. Root is the acquisition of the rights of the super user of the operating system, where you can read / write in the OS partition, for example, replace the OS image (which, therefore, allows several different operating systems to be used).
3. Internal phone storage
Internal phone storage is the second amount of memory for user data, including downloaded applications and their stored data (from RAM). The free space in the Internal phone storage becomes smaller when you install more applications. There may come a time when you can not install applications – when the Internal phone storage has too little free space; then you need to remove unnecessary programs.
4. MicroSD / SDHC
This is the only type of memory that the user can expand. It is similar to an external storage, for example, an external hard disk (External HDD) for a computer. This memory can be seen in the “Settings” -> “Storage” section. On the microSD-card you can store any data (movies, music, photos and so on). Some of the installed applications can be transferred from the internal memory to the SD card: this saves valuable internal memory space. If you want, you can replace the SD-card (for example, to another with a large volume). To do this, do not forget to unmount (“unmount”) the current SD card before physically removing it: “Settings” -> “Storage” -> Press the “Extract” button of the desired SD card. The inserted new SD card will be automatically installed (“mounted”).
About the battery of the device
Android is an extremely energy-intensive system, so the problem of rapid battery consumption is very urgent.
When choosing a smartphone or tablet, it is important to pay attention to the capacity of the battery, which shows how long the battery can power the device. The larger the capacity, the longer it will be able to work the device until the next charge. Typically, the capacity is specified in milliampere-hours.
In Android, there are many factors that affect battery consumption, below are listed the most common:
1. The display is too bright. If you go into the statistics of using the battery in your device\’s settings, you can find that often in the first positions the screen is specified, especially if you are actively using the smartphone. The fact is that the more brightness of the screen is set in the settings, the more the battery consumption will be, so if you want to save a little bit of power, reduce the brightness to an acceptable one or turn on the function (if any) of automatically adjusting the brightness for illumination.
2. Unused device modules. When you turn on additional modules on your device, such as Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, GPS and others, the system starts to consume more energy to maintain them. Therefore, the ideal solution in this case will include these modules only if necessary and turn off if they are not currently in use.
3. Energy-intensive applications. Very often, applications perform some of their work in the background, regardless of the user, while they can access not only the system, but also send and receive data over the network. All these operations require additional energy costs, so if there are many such applications, this greatly affects the battery consumption. Therefore, you should check applications for energy costs, stop them if they are not needed at the moment, or even delete them if the damage from them is more than good. In addition, it is important to remember that mobile games also consume the battery very much.
4. High temperature. Batteries react very negatively to a rise in temperature. For example, at a temperature of 0°C, a lithium-ion battery will lose 6% of its capacity per year, and at 25°C it will lose 20%. Therefore, if you want to preserve the original capacity of the battery, you should avoid storing the device in places with high temperatures.
5. Age of the battery. Batteries on average live about 4-5 years for the simple reason that over time their characteristics are gradually deteriorating. The aging of the batteries is inevitable, but it is important not to accelerate this process (in fact, the 4th factor directly accelerates the degradation of the battery). If this moment has come and the charge of your battery is enough for one hour of working with the device, just replace it with a new one.
Stopping the application
Often there is a situation where an application that is not needed by the user at the moment is running in the background and consumes battery power and device memory.
Such applications can be turned off – the application is not deleted, but it seems to “fall asleep” and does not start until it is turned on. Disabling saves battery power, space in the device memory and Internet traffic.
To turn off the application, go to Settings, go to Applications and then click “Disable” in the selected application.
It may also be that the button is inactive, which means that the application is needed for the system to work and it can not be turned off.
Secret codes
In Android, there are various codes that are hidden from ordinary users and allow you to get any additional information about the device or conduct tests. Here is a list of some of these codes, but they are not universal: some devices support the right command, while others may not support it.
- *#06# — information about IMEI smartphone
- *#*#4636#*#* — Wi-Fi, battery, and usage statistics
- *#*#8255#*#* — testing Google Talk service
- *#*#7594#*#* — if you enter this combination, then after that, when you press the power button, the smartphone will immediately turn off, without the menu offer
- *#*#44336#*#* — information about PDA, CSC, build time and other data about the smartphone
- *#*#232338#*#* — MAC Address Wi-Fi
- *#*#7780#*#* — instant reset to the factory settings (Hard Reset). Deletes only applications
- *2767*3855# — instant reset of factory settings, but unlike the previous way Android completely re-installed
- *#*#1234#*#* or *#12580*369# — information about the firmware of the device
- *#*#1111#*#* — information about the FTA software version
- *#*#2222#*#* — information about FTA hardware version
- *#*#0283#*#* — Loopback test
- *#*#0*#*#* — screen test
- *#0*# — testing of various components: screen, camera, speakers, vibration, microphone and other
- *#*#0673#*#* or *#*#0289#*#* — audio test
- *#*#0842#*#* — vibration and backlight test
- *#*#232339#*#* or *#*#526#*#* — test wireless network
- *#*#1472365#*#* — GPS test
- *#*#1575#*#* — detailed GPS test
- *#*#232331#*#* — Bluetooth test
- *#*#232337#*#* — show Bluetooth address
- *#*#2663#*#* — touch screen version
- *#*#2664#*#* — touch screen test
- *#*#0588#*#* — motion sensor test
- *#*#7262626#*#* — GSM signal test
- *#197328640# — transition to service mode
- *#*#3264#*#* — memory RAM version
- *#*#8351#*#* — activation of the voice dial registration mode
- *#*#8350#*#* — turn off the voice dial registration mode
- #*5376# — delete all SMS
- *#2222# — Android firmware version
- #*2562#, #*3851#, #*3876# — reboot smartphone, tablet
- *#34971539# — full information about the cameras and updating their firmware
- *#*#273283*255*663282*#*#* — fast backup of media files
- *#*#4636#*#* — fast backup of media files
- **05***# — unlock PUK on Sony
- 3845#*855# — service menu on LG G3
- *#0011# — service menu on Samsung Galaxy S4
- ##778 (+call button) — displays the EPST menu (for Samsung)
- ##3424# — diagnostic mode (for HTC)
- ##3282# — EPST (for HTC)
- ##8626337# — VOCODER (for HTC)
- ##33284# — network status technical data (for HTC)
- ##7738# — revision protocol (for HTC)